CI/CD with GitHub Actions: Automate Your Workflow
A complete, hands-on guide to setting up CI/CD pipelines with GitHub Actions, from basics to advanced automation and deployment strategies.
⚡ CI/CD with GitHub Actions: Automate Your Workflow
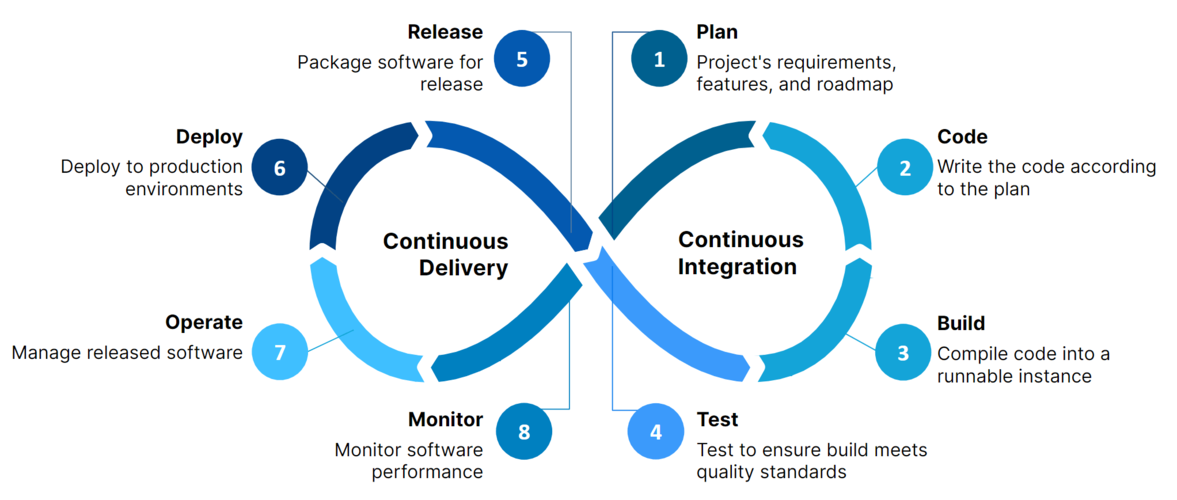
Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) are essential for modern software teams. GitHub Actions makes it easy to automate your workflows, from running tests to deploying code. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll cover everything you need to know to set up robust CI/CD pipelines with GitHub Actions.
🚀 What is CI/CD?
- Continuous Integration (CI): Automatically build and test your code every time you push changes.
- Continuous Deployment (CD): Automatically deploy your code to production after passing tests.
Why Use CI/CD?
- Faster feedback: Catch bugs early.
- Consistency: Automate repetitive tasks.
- Reliability: Reduce human error.
- Speed: Ship features faster.
🏗️ Introduction to GitHub Actions
GitHub Actions is a workflow automation tool built into GitHub. It lets you define custom workflows using YAML files in your repository.
Key Concepts
- Workflow: Automated process triggered by events (push, pull request, etc.).
- Job: A set of steps that run in the same environment.
- Step: A single task (run a script, check out code, etc.).
- Action: A reusable extension for common tasks.
📝 Creating Your First Workflow
- Create a
.github/workflows/ci.ymlfile in your repo. - Add the following:
name: CI
on: [push, pull_request]
jobs:
build:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
- name: Set up Node.js
uses: actions/setup-node@v3
with:
node-version: '18'
- name: Install dependencies
run: npm install
- name: Run tests
run: npm test
🧩 Advanced Workflows
1. Matrix Builds
Test your code on multiple Node.js versions:
strategy:
matrix:
node: [16, 18, 20]
jobs:
build:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
strategy:
matrix:
node: [16, 18, 20]
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
- uses: actions/setup-node@v3
with:
node-version: ${{ matrix.node }}
- run: npm install
- run: npm test
2. Caching Dependencies
Speed up builds by caching node_modules:
- name: Cache node modules
uses: actions/cache@v3
with:
path: ~/.npm
key: ${{ runner.os }}-node-${{ hashFiles('**/package-lock.json') }}
restore-keys: |
${{ runner.os }}-node-
3. Deploying to Vercel/Netlify
Use deployment actions to automate production releases.
🏃♂️ Real-World CI/CD Scenarios
1. Linting and Formatting
- name: Lint code
run: npm run lint
2. Running End-to-End Tests
Integrate Cypress or Playwright for E2E testing.
3. Building Docker Images
- name: Build Docker image
run: docker build -t my-app .
4. Publishing to npm
- name: Publish to npm
run: npm publish
env:
NODE_AUTH_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.NPM_TOKEN }}
🛡️ Security Best Practices
- Use GitHub Secrets for sensitive data.
- Limit permissions for workflows.
- Review third-party actions for security.
🧠 Optimizing Your Pipelines
- Parallel jobs: Run jobs in parallel to speed up builds.
- Reusable workflows: Share common workflows across repos.
- Manual triggers: Use
workflow_dispatchfor manual runs.
🏆 Case Study: Scaling CI/CD for a SaaS Startup
A SaaS team automated their entire release process with GitHub Actions:
- Reduced deployment time from hours to minutes
- Fewer production bugs
- Happier developers
📝 Troubleshooting GitHub Actions
- Workflow not running? Check your YAML syntax and triggers.
- Job failures? Review logs for errors.
- Permission issues? Verify secrets and access rights.
📚 Further Reading
🎯 Conclusion
GitHub Actions makes CI/CD accessible to everyone. By automating your workflows, you can ship faster, catch bugs earlier, and focus on building great products.
Happy automating! ⚡
This blog is part of a series on modern web development tools. Check out our guides on Docker, Prisma, TypeScript, and GraphQL!